Thyroid Health Tips
Do you know what your thyroid is, where it is, and what it does? You’re not alone if you answered with a no. Your thyroid gland is shaped a little like a butterfly shaped gland and plays a vital role in your overall thyroid health. You can find this small endocrine gland toward the front of your neck in the lower portion, just below the Adam’s apple. You can’t feel or see this gland if it’s healthy and functioning like it should be. It’s usually a good indicator that something is wrong if you can feel it or even see it when you look, which may suggest a thyroid nodule or goiter.
This small endocrine gland plays a huge role in helping regulate several systems in your body.
It is part of the endocrine system, the body’s communication network, where glands house hormones that act as chemical messengers and transmit information to various parts of the body. Every single cell in the body relies on thyroid hormone for proper function.
It links directly to your nervous system, menstrual cycle, body weight, cholesterol levels, muscle strength, and your heart rate and breathing. Proper thyroid hormone balance helps maintain metabolism, energy levels, and mental clarity.
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE THYROID?
- Growth and development of children
- Muscle functioning
- Heart muscle functioning in pumping effectively and efficiently
- Digestion and excretion of food
- Hair, skin and nail strength
- Development of the brain
- Growth and strength of bones
- Development of the body’s organs.
The thyroid gland works closely with other endocrine glands, such as the pituitary gland, to regulate thyroid hormone production and maintain a steady metabolic rate. When thyroid function becomes unbalanced, it can affect nearly every organ system in the body.
WHAT IS IODINE’S ROLE IN THYROID HEALTH
Your Thyroid Needs a Constant Supply of Iodine to function properly.
Your Thyroid Needs a Constant Supply of Iodine to function properly.
The thyroid gland requires iodine to produce thyroid hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). You need enough iodine in your diet to help support a healthy thyroid function, because your thyroid uses this mineral to create hormones that regulate metabolism, energy, and growth. Unfortunately, your body doesn’t produce iodine by itself.
Iodine is supplied by eating foods that contain good levels of it. You can get iodine from bread and iodized table salt in the United States. These foods were originally specially formulated with iodine in 1924 to combat the wave of iodine deficiency found all over the United States. Not having enough iodine in your diet can lead to goiter, and in severe cases, cretinism (severe developmental issues in infants). It can also lead to hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid cannot get enough iodine to produce the hormones your body needs to function properly.
Maintaining the right amount of iodine supports overall thyroid gland health, reduces the risk of thyroid nodules, and helps your thyroid hormone levels remain stable. People with symptoms like fatigue, weight fluctuations, or neck swelling should consider thyroid function tests, thyroid ultrasound imaging, or even a fine needle aspiration biopsy if nodules are detected. Early detection allows your doctor to create a personalized treatment plan for long-term thyroid health.
THYROID DISEASE SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Did you know that roughly 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disease? There are even more people who don’t have any idea that there is a problem with their thyroid. When the thyroid is healthy, it quietly performs its task. But when diseased, the problems can become annoying at best and life threatening at worst.
Only 4–6% of thyroid nodules are actually malignant, or cancerous. Although the incidence of thyroid cancer has been rising over the past 10 years, the mortality rate has stayed the same, meaning fewer and fewer people die of it.
The majority of thyroid cancer is well differentiated, meaning that it is easily treatable. The most common of these cancers is Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma, often diagnosed through a thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy or ultrasound guided biopsy.
There are several medical conditions of thyroid disease, each with its own set of signs and symptoms. These may include hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer, all of which require different diagnostic approaches and follow-up testing. Regular thyroid screening, ultrasound imaging, and biopsy procedures can help with early thyroid cancer detection and appropriate treatment planning.
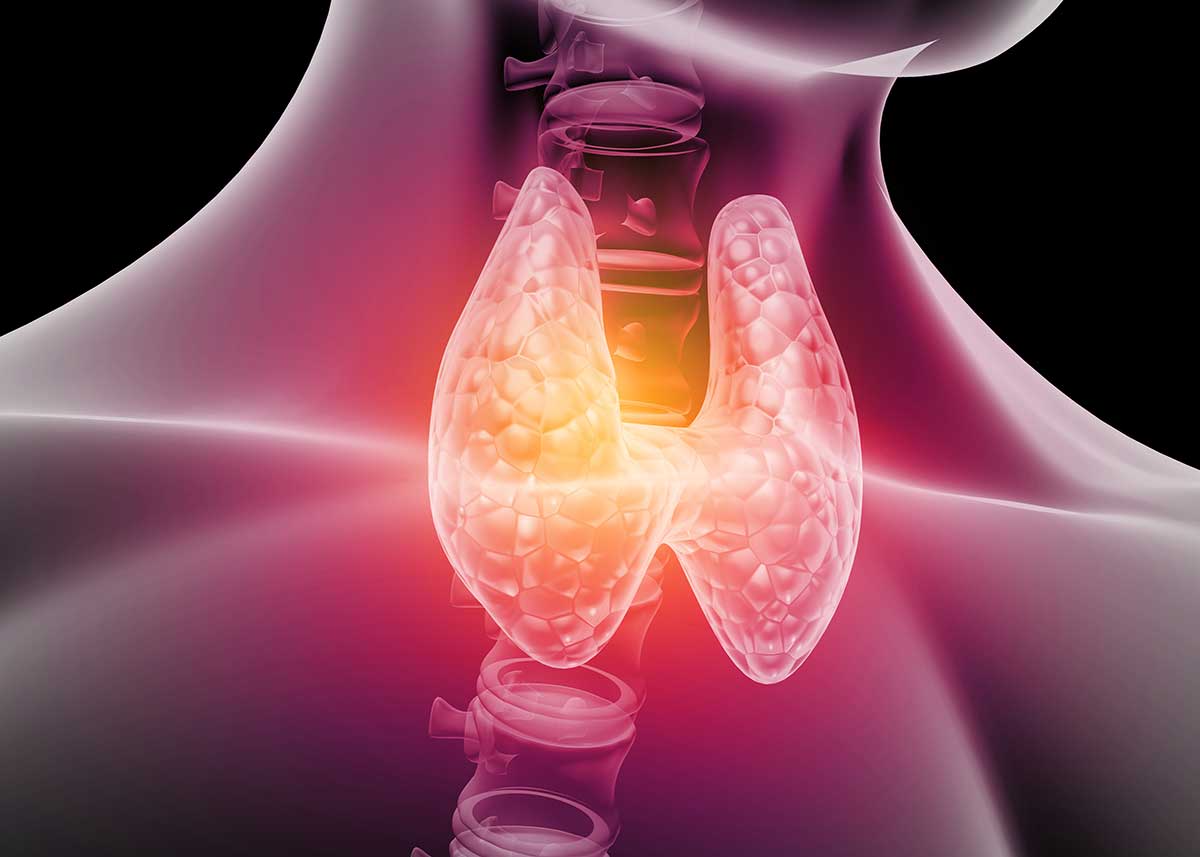
What are the Different Types of Thyroid Diseases?
What is Hypothyroidism?
- Hypothyroidism is a condition where your gland isn’t producing enough hormone.
- Symptoms include feeling cold, lethargic, dry, weight gain, constipation, slow heartbeat, depression, memory problems.
- Causes of hypothyroidism besides lack of iodine can be from an autoimmune disorder called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Sometimes it can develop transiently during or after pregnancy.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
- Hyperthyroidism is a condition where your gland is producing too much hormone for your body to handle. Common signs of hyperthyroidism include things like trouble sleeping, losing weight, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and feeling too warm.
- Causes can be due to a growth of a nodule acting on its own (autonomous), overproducing hormones or also from another autoimmune condition called Grave’s Disease. Some people with this condition notice that their eyes are bulging.
What are Goiters?
- A goiter means that the thyroid gland is enlarged. It could be due to too much or too little thyroid hormone. If you have seen any 16th or 17th century European paintings many of the subjects wore a “ruff” which was a collar born into fashion to initially cover up goiter.
What are Thyroid nodules?
- Simply put, a nodule is a lump. Most thyroid nodules are benign (non-cancerous) and harmless. Many of them go unnoticed until your doctor finds one on yearly physical exam or during imaging studies for something else. Sometimes they cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing dry foods, because the nodule may be large and press against the esophagus. In addition, it may also cause hoarseness or difficulty breathing, if it presses on the trachea (windpipe). Sometimes only one is found, sometimes there are many (also called multinodular goiter).

THYROID DISEASE SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Did you know that roughly 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disease? There are even more people who don’t have any idea that there is a problem with their thyroid. When the thyroid is healthy, it quietly performs its task. But when diseased the problems can become annoying at best, and life threatening at worst.
Only 4-6% of thyroid nodules are actually malignant, or cancerous. Although the incidence of thyroid cancer has been rising over the past 10 years, the mortality rate has stayed the same, meaning, fewer and fewer people die of it.
The majority of thyroid cancer is well differentiated, meaning that it is easily treatable. The most common of these cancers is Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.
There are several medical conditions of thyroid disease, each with its own set of signs and symptoms.
What are the Different Types of Thyroid Diseases?
What is Hypothyroidism?
- Hypothyroidism is a condition where your gland isn’t producing enough hormone.
- Symptoms include feeling cold, lethargic, dry, weight gain, constipation, slow heartbeat, depression, memory problems.
- Causes of hypothyroidism besides lack of iodine can be from an autoimmune disorder called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Sometimes it can develop transiently during or after pregnancy.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
- Hyperthyroidism is a condition where your gland is producing too much hormone for your body to handle. Common signs of hyperthyroidism include things like trouble sleeping, losing weight, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and feeling too warm.
- Causes can be due to a growth of a nodule acting on its own (autonomous), overproducing hormones or also from another autoimmune condition called Graves’ Disease. Some people with this condition notice that their eyes are bulging.
What are Goiters?
A goiter means that the thyroid gland is enlarged. It could be due to too much or too little thyroid hormone. If you have seen any 16th or 17th century European paintings many of the subjects wore a “ruff” which was a collar born into fashion to initially cover up goiter.
What are Thyroid nodules?
Simply put, a nodule is a lump. Most thyroid nodules are benign (non-cancerous) and harmless. Many of them go unnoticed until your doctor finds one on yearly physical exam or during imaging studies for something else. Sometimes they cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing dry foods, because the nodule may be large and press against the esophagus. In addition, it may also cause hoarseness or difficulty breathing, if it presses on the trachea (windpipe). Sometimes only one is found, sometimes there are many (also called multinodular goiter).
THYROID CANCER BIOPSY FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION
To find out whether you have a cancerous lump of the thyroid a FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNA) biopsy is needed. Using ultrasound imaging as a guide, a thin needle is used to gather a small sample of the thyroid nodule to determine (diagnose) whether it is malignant or not.
The procedure involves inserting the needle carefully through the skin and into the thyroid nodule, ensuring precision at the biopsy site. This is a minimally invasive procedure that can be done in an office outpatient setting with local anesthesia. The actual procedure itself takes only a few minutes. If done by a cytopathologist, the sample can be immediately viewed under the microscope to see if there is enough material, and sometimes a preliminary result of the thyroid biopsy can be given right then and there.
This test helps doctors decide whether a surgical biopsy or other treatment plan is needed. Afterward, your doctor will provide specific instructions for care of the biopsy site to help ensure smooth healing.
Early detection is very important and can sometimes be the difference between life or death. If you notice that something is off with your health or you experience any of these symptoms, play it safe and make an appointment to discuss your concerns with your doctor. Paying attention and knowing your body not only helps with early thyroid cancer detection, but also other underlying medical conditions that could be affecting your daily life.
Talk to your doctor today about a thyroid nodule biopsy or FNA thyroid biopsy so they can refer you to our clinic. Take control of your thyroid gland health and trust experienced specialists who use thyroid ultrasound guided biopsy for accurate results.
Our office provides expert care in thyroid cancer diagnosis, thyroid cancer treatment, and thyroid nodule evaluation for patients across Oceanside and surrounding areas. Schedule your consultation with a thyroid specialist near me and get the answers you need to protect your health.
Dr. Celina Nadelman, M.D., is one of very few doctors in the U.S. to uniquely serve as both a board certified cytopathologist and a fine needle aspiration (FNA) specialist. In addition to operating her own FNA clinic and in-office laboratory practice in Beverly Hills, California, Dr. Nadelman performs the same dual-role services at Los Angeles County’s Martin Luther King, Jr. Outpatient Center, and is also a clinical instructor at UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine Greater Los Angeles Training Cytotechnology Consortium.
CELINA NADELMAN, M.D.
WE ARE HERE TO HELP
Request an appointment with The Cancer Biopsy Doctor, Celina M. Nadelman, M.D. today.